Data encryption, also known as ciphering, is the conversion of data using algorithms so that it is illegible or at least very difficult to decipher. Decryption "translates" the data back into its original form, making it available only to someone who holds the correct decryption key. This process is used when entering passwords or payment information for example. But why is data encryption ever needed? And how does it work?
Table of contents:- Why encrypt data
- Global policies regarding data encryption
- Types of Data encryption
- Data encryption in-transit, at-rest, and in a cloud
- Tips for encryption passwords
- Data encryption with Microsoft 365
Why encrypt data?
Data encryption sounds like a lot of work. Why bother? Actually, it is not that much of a hassle: you already use encryption when you visit an HTTPS webpage as you are right now.
The main reason for encryption is data protection. You would not send a contract to someone by mail without protecting it from the eyes of third parties with an envelope. In case of e-mails, applications such as Microsoft Outlook can take care of the envelope with their integrated security measures (provided you enable them). Data encryption translates the message into hieroglyphics that can only be read by the intended recipient. Even if a data thief opens your envelope, they can then do very little with the contents.
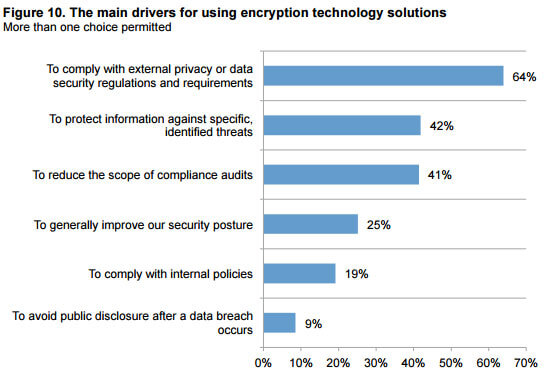
According to a Health IT Security's survey, compliance with regulations regarding data security is one of the main reasons for data encryption, followed by protection against cybercrime.
The threat of cyberattacks and data theft is on the rise, causing billions of dollars in damage for companies every year. According to Statista, lack of cyber security training and naivete are two of the top three reasons for a ransomware infection.
Global policies regarding data encryption
The laws regarding data security and data encryption differ widely. In the US, there a variety of laws more or less covering data protection at Federal, State and local levels.
Protection Regulation or GDPR – enforced by data protection authorities in each of the 27 EU member countries. The GDPR covers anyone – organization or individual – that processes or controls personal data about anyone present in the EU (citizen or not). In addition, each EU member country may enforce additional data security requirements. Violations can incur significant penalties.
According to article 32 of the GDPR:
Taking into account the state of the art, the costs of implementation and the nature, scope, context and purposes of processing as well as the risk of varying likelihood and severity for the rights and freedoms of natural persons, the controller and the processor shall implement appropriate technical and organisational measures to ensure a level of security appropriate to the risk, including inter alia as appropriate.
The GDPR recommends data encryption and favors it when it comes to sanctions for data breaches or theft. It stipulates that theft or loss of personal data must be logged for inspection by the relevant data protection authority, and reported to the affected person if there is potential risk to the affected person’s rights or freedoms.
The requirements of the General Data Protection Regulation may sound excessive to some, but they lead to fewer data breaches compared to many other countries. Also, the GDPR provides good guidelines for any organization that wants to manage its data properly. So it makes good business sense to understand and align with the GDPR’s requirements.
Differences in handling data protection leads to some difficulties when it comes to data exchange between the EU and the US. European companies that store data on US based cloud services or servers could face severe sanctions as a result of an offense under the GDPR.
The importance of the topic of data security and GDPR compliance has increased with the spread of home office security and mobile working. Do you wonder how to set up your Digital Workplace securely? Then our eBook is interesting for you!
What types of data encryption are out there?
There are two so-called "cryptographic" methods for data encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Sounds like geometry at first, but in this case, it has to do with the method of decryption.
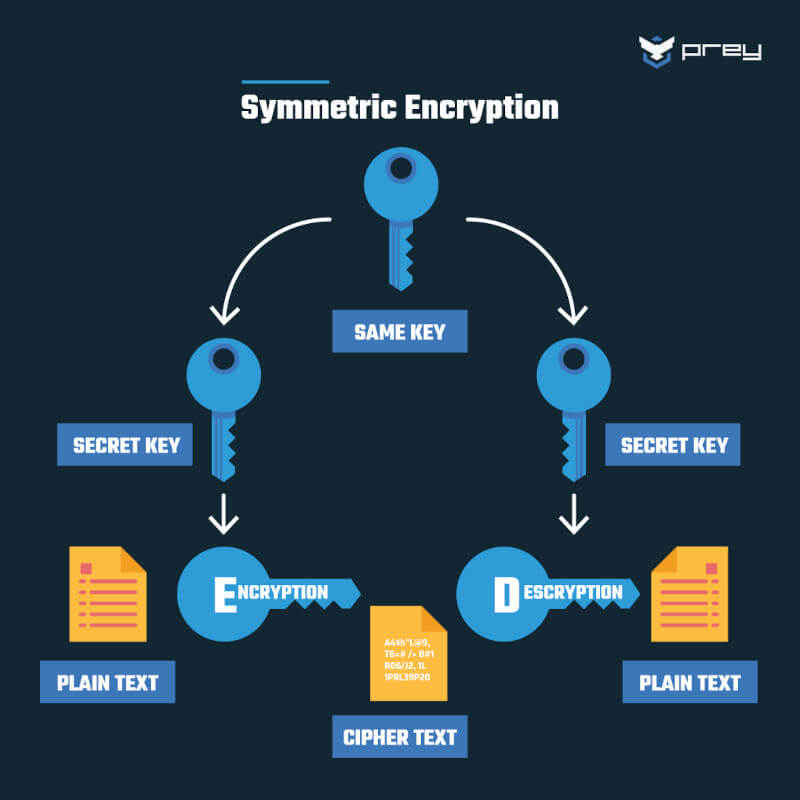
Source: PreyProject
Symmetric encryption uses the same key for encryption and decryption. If you want to send data, you must also transmit the key to the recipient in a secure manner. Asymmetric encryption is therefore somewhat simpler for data transfer.
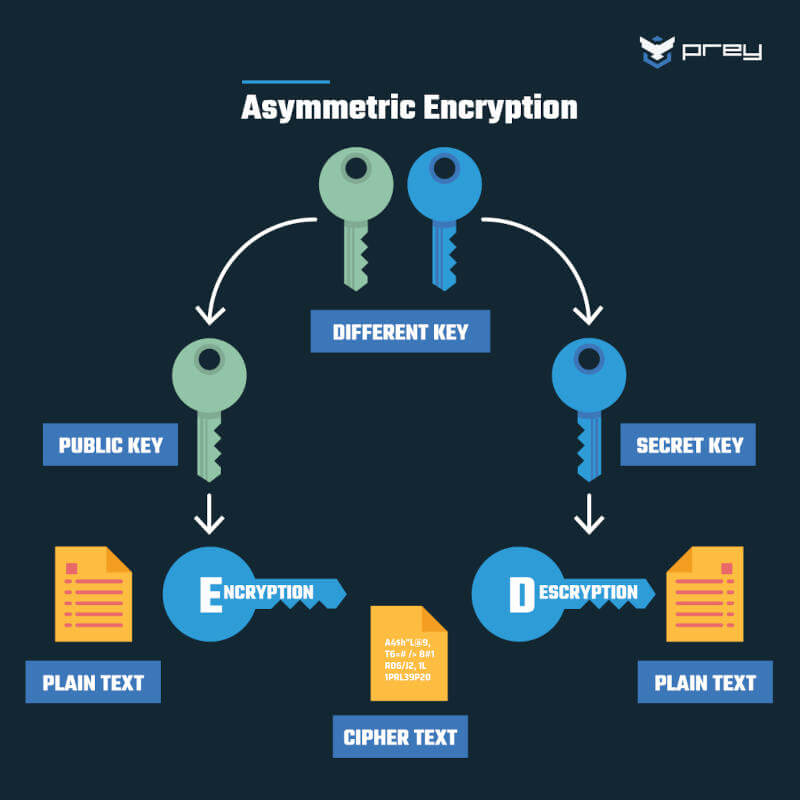 Source: PreyProject
Source: PreyProject
In asymmetric encryption, there are two keys. First, a so-called "public key" is used. It is available to any person who wants to encrypt data. After the data has been transmitted, it is decrypted by a secret key that the recipient holds. A good example of this process is sending e-mails. Any person who knows your e-mail address can send you an e-mail to which only you have access.
Data encryption in-transit, at-rest, and in a cloud
Encryption is possible no matter where your data is located – at rest on your server or in a cloud, or in transit.
“At rest” means that your data is on a storage medium. Thieves often assume that the more important data is located there. So, despite drive security measures, there is a risk such as physical theft. However, with encryption your data is safe from prying eyes.
If you store your data in a cloud, you should look into the encryption measures your service providers use. A particular focus should be on implementation of internal requirements, but also conformity to legal regulations in the region or industry. Unfortunately, most organizations do not encrypt any or all of their at-rest data.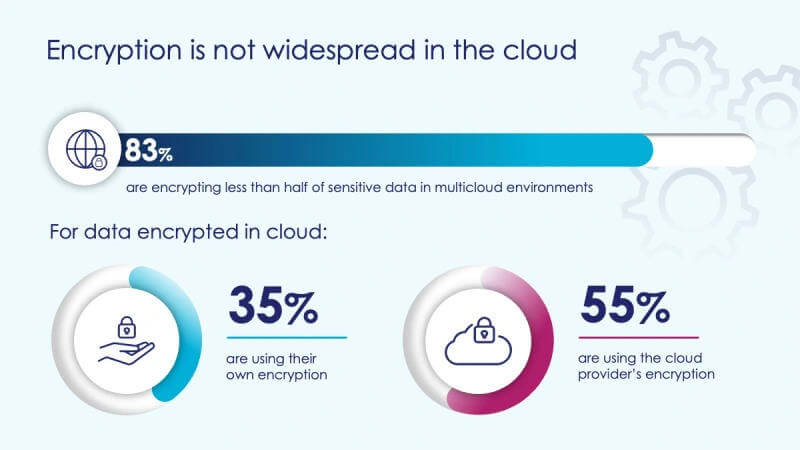
Source: Venturebeat
If the provider's measures are not sufficient, you can of course encrypt your data yourself before uploading, like the 35% shown. Another challenge when using cloud providers is management of encryption keys, which must be adequately secured and managed.
Are you unsure whether to store your data on-premise or in a cloud? We have summarized some more useful information for you!
In transit, data is at a higher risk than in storage. Here, security depends not only on the precautions of the storage location, but also on the transfer service. Encrypting data while in transit is called end-to-end encryption.
Tips for passwords for data encryption
If you use passwords for data encryption and want to pass them on, here are some tips for secure passwords:- At least 12 characters: the longer the better
- Variety: Use upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters
- No names of family members or pets
- No birth dates of your own or family members
- Never send a password to someone in the same message where you include the username!
- No numerical or letter sequence like abcd1234

Data encryption with Microsoft 365
Microsoft has implemented numerous data security and data encryption tools. It secures your at-rest and in-transit data in Microsoft's own messenger services, such as Microsoft Teams, Outlook and Skype. We also summarized more information on how Microsoft Information Protection protects your data.
- 7-Zip: sometimes even comes pre-installed. Encrypts files or folders with passwords
- Boxcryptor: Encryption of data before cloud upload and key management.
- KeePassXC: Encryption and password management
- Aomei Backupper Pro: Backup encyrption (1 year license)
Did you know that empower® is a Microsoft partner? Our Microsoft Office solutions provide maximum security for your documents and are compatible with all Microsoft updates.
Learn more about data security and data management with empower® and make an appointment easily and non-binding.
You May Also Like
Related articles

Data security with Microsoft Information Protection

On-Premises vs Cloud: Advantages and Disadvantages



